
 |
|
#1
|
||||
|
||||
|
All you need to know about STD
Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD)
A sexually transmitted disease (STD), also known as a sexually transmitted infection (STI), or venereal disease (VD), is an illness that has a significant probability of transmission between humans by means of human sexual behavior, including vaginal intercourse, oral sex, and anal sex. While in the past, these illnesses have mostly been referred to as STDs or VD, in recent years the term sexually transmitted infections (STIs) has been preferred, as it has a broader range of meaning; a person may be infected, and may potentially infect others, without showing signs of disease. Some STIs can also be transmitted via the use of IV drug needles after its use by an infected person, as well as through childbirth or breastfeeding. Sexually transmitted infections have been well known for hundreds of years. need help??? Speak to a counselor for free, dail 1800 252 1324 (DSC) more info @ http://www.dsc-sexualhealth.com.sg/showpage.asp?id=58 What's the difference between a bacterial and viral STD? click here to read about it Bacterial 1. Chlamydia | Chlamydia in woman 2. Gonorrhea (clap, drip) 3. Syphilis 4. Chancroid Viral 7. Herpes 8. Gential Warts 9. Hepatitis B 10. Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) | More info here 11. HIV/Aids others/parasitic/Inflammatory Disease 12.Pubic Lice | Pubic Lice 13.Trichomoniasis 14. Vaginitis 15. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) | more info here 16. UTI(Urinary tract infection) |more | more | more | more | more | more
__________________
You are my forum, my only forum, you make me happy, when skies are grey... Sex health related questions click here. WOMEN'S CHARTER click here Sg law on sex related matters click here Last edited by Big Sexy; 19-05-2011 at 08:05 AM. |
|
#2
|
||||
|
||||
|
Re: All you need to know about STD ( with pictures)
Syphilis
Source :http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0002303/ Source : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Syphilis what is Syphilis Syphilis is an STD caused by the bacteria Treponema pallidum. It's sometimes called the "great imitator" because early symptoms are so similar to other diseases. The disease proceeds through stages -- In primary syphilis, a chancre -- an open sore that's usually painless -- appears, most commonly on the genitals, usually 10-90 days after exposure. In secondary syphilis, a skin rash appears, on any part of the body, including palms of hands & soles of feet. In tertiary syphilis, the disease spreads to internal organs, where it can do serious damage. A pregnant woman can pass the disease on to her child. Having syphilis makes a person more susceptible to HIV. Early diagnosis is important because syphilis is readily treatable with antibiotics. Causes, incidence, and risk factors Syphilis is a sexually-transmitted infectious disease. The bacteria that cause it spread through broken skin or mucous membranes. Pregnant mothers infected with the disease can pass it to the baby developing in their womb. This is called congenital syphilis. Syphilis is widespread in the United States. It mainly affects sexually active adults ages 20 to 29. Syphilis has several stages. Primary syphilis is the first stage. Painless sores ( chancres) form at the site of infection about 2-3 weeks after you are first infected. You may not notice the sores or any symptoms, particularly if the sores are inside the rectum or cervix. The sores disappear in about 4-6 weeks, even without treatment. The bacteria become dormant (inactive) in your system at this stage. For more specific information about this type of syphilis, see primary syphilis. Secondary syphilis occurs about 2-8 weeks after the first sores form. About 33% of those who do not have their primary syphilis treated will develop this second stage. These symptoms will often also go away without treatment and again, the bacteria become dormant (inactive) in your system. For more specific information about this type of syphilis, see secondary syphilis. Tertiary syphilis is the final stage of syphilis. The infection spreads to the brain, nervous system, heart, skin, and bones. The dormant bacteria may be detectable either by seeing the damage they cause to a part of the body, or through a blood test for syphilis. For more specific information about this type of syphilis, see tertiary syphilis.  Symptoms The symptoms of syphilis depend on the stage of the disease. Many people do not have symptoms. In general, painless sores and swollen lymph nodes are possible symptoms of primary syphilis. Those with secondary syphilis may also have fever, fatigue, rash, aches and pains, and loss of appetite, among other symptoms. Tertiary syphilis causes heart, brain, and nervous system problems. Signs and tests Blood tests can be done to detect substances produced by the bacteria that cause syphilis. The older test is the VDRL test. Other blood tests may include RPR and FTA-ABS. Treatment Antibiotics are an effective treatment for syphilis. The antibiotic of choice is penicillin. The dose and how it's given (into a muscle or into a vein) depend on the stage of syphilis. Doxycycline may be used as an alternative treatment in individuals who are allergic to penicillin. Several hours after treatment of early stages of syphilis, you may have a reaction called Jarish-Herxheimer reaction. Symptoms of this reaction include: Chills Fever General feeling of being ill General joint aches General muscle aches Headache Nausea Rash These symptoms usually disappear within 24 hours. You must have follow-up blood tests at 3, 6, 12, and 24 months to make sure the infection is gone. You should avoid sexual conduct until two follow-up tests show that the infection has been cured. Syphilis is extremely contagious through sexual contact in the primary and secondary stages. Syphilis is a reportable infection. That means that doctors must report any cases of syphilis to public health authorities, so that potentially infected sexual partners may be identified and treated. Expectations (prognosis) With prompt treatment and follow-up care, syphilis can be cured. Late-stage syphilis can lead to long-term health problems, despite therapy. Syphilis increase the risk of HIV transmission by 2 to 5 times and co infection is common (30-60% in a number of urban centers).[1][2] Untreated it has a mortality of 8% to 58% with a greater death rate in males.[1] Complications Complications of untreated syphilis include: Damage to the skin and bones Heart and blood vessel problems, including inflammation and aneurysms of the aorta Neurosyphilis Prevention If you are sexually active, practice safe sex and always use condoms. All pregnant women, people with HIV, and others at increased risk for having syphilis should be screened for syphilis. Epidemiology Syphilis is believed to have infected 12 million people in 1999 with greater than 90% of cases in the developing world.[2] It affects between 700,000 and 1.6 million pregnacies a year resulting in spontaneous abortions, stillbirths, and congenital syphilis.[6] In Sub Saharan Africa syphilis contributes to approximately 20% of perinatal deaths.[6] In the developed world, syphilis infections were in decline until the 1980s and 1990s due to widespread use of antibiotics. Since the year 2000, rates of syphilis have been increasing in the USA, UK, Australia and Europe primarily among men who have sex with men.[2] This is attributed to unsafe sexual practices.[2] Increased rates among heterosexuals have occurred in China and Russia since the 1990s.[2]  Model of the head of a patient with tertiary syphilis.
__________________
You are my forum, my only forum, you make me happy, when skies are grey... Sex health related questions click here. WOMEN'S CHARTER click here Sg law on sex related matters click here Last edited by Big Sexy; 04-05-2011 at 09:33 AM. |
|
#3
|
||||
|
||||
|
Re: All you need to know about STD ( with pictures)
GENITAL WARTS
source: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001889/ source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genital_wart Causes, incidence, and risk factors The virus that causes genital warts is called human papilloma virus (HPV). More than 70 different types of HPV exist. Several types of HPV cause genital warts, which may be found on the penis, vulva, urethra, vagina, cervix, larynx, and around and in the anus. Other types of HPV cause common or flat warts on other parts of the skin, such as the hands. However, warts on the hands or other parts of the body do not cause genital warts. HPV infection around the genitals is common, although most people have no symptoms. Even if you do NOT have symptoms, however, you must be treated to prevent complications and spreading the condition to others. In women, HPV can invade the walls of the vagina and cervix. These warts are flat and not easy to see without special procedures. Certain types of HPV can lead to precancerous changes in the cervix, cervical cancer, or anal cancer. These are called high-risk types of HPV. The following are important facts about how HPV and genital warts can be spread: HPV infection is passed from one person to another through sexual contact involving the skin of the anus, mouth, or vagina, or the mucus membrane. It is possible for genital warts and HPV to spread, even when no warts can be seen. You may not see warts for at least 6 weeks to 6 months after becoming infected with HPV. It may also take longer, even years, so when you first notice genital warts, it does not mean that you or your partner has had sexual contact with someone outside of your relationship. Not everyone who has been exposed to the HPV virus and genital warts wil develop them. The following factors put you at higher risk for getting genital warts, having them spread more quickly, having them return, or having other complications of HPV: Having multiple sexual partners Not knowing whether someone you had sex with had STIs Becoming sexually active at an early age Using tobacco and alcohol Having stress and other viral infections (such as herpes) at the same time Being pregnant Having an immune system that does not work well, such as during cancer treatment or AIDS If a child has genital warts, you should suspect sexual abuse as a possible cause. Symptoms Genital warts can be raised or flat, and are usually flesh-colored. They may appear as cauliflower-like growths. Sometimes they are so small and flat that they cannot be seen with the naked eye. Common places to find genital warts: Females most often have warts inside or around the vagina or anus, on the skin around these areas, or on the cervix. Males most often have warts on the penis, scrotum, groin area, or thighs, as well as inside or around the anus in those who have anal intercourse. Both males and females may have warts on the lips, mouth, tongue, palate, or throat (larynx) Other symptoms are rare, but may include: Increased dampness or moisture in the area of the growths Increased vaginal discharge Itching of the penis, scrotum, anal area, or vulva Vaginal bleeding, with or after sexual intercourse Signs and tests Flesh-colored to white, flat or raised, single or clustered warts may be seen anywhere on the genitals. In women, a pelvic examination may reveal growths on the vaginal walls or cervix. Magnification (colposcopy) may be used to see lesions that are invisible to the naked eye. The tissue of the vagina and cervix may be treated with acetic acid (dilute vinegar) to make the warts visible. A Pap smear may note changes caused by HPV. Women with these types of changes often need more frequent Pap smears for a period of time. An HPV DNA test can identify whether you have a high-risk type of HPV that is known to cause cervical cancer. This test may be done: As a screening test for women over age 30 In women of any age who have a slightly abnormal Pap test result Treatment Genital warts must be treated by a doctor. Do NOT use over-the-counter remedies meant for other kinds of warts. Your doctor may treat genital warts by applying a skin treatment in the office. Or, the doctor may prescribe a medication that you apply at home several times per week. These treatments include: Imiquimod (Aldara) Podophyllin and podofilox (Condylox) Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) Surgical treatments include: Cryosurgery Electrocauterization Laser therapy Surgical excision (cutting them out) If you develop genital warts, all of your sexual partners must be examined by a health care provider and treated if genital warts are found. After your first treatment, your doctor will schedule follow-up examinations to see if the warts have returned. Women who have had genital warts, and women whose partners have ever had genital warts, should have Pap smears at least once a year. For warts on the cervix, women may need to have Pap smears every 3 to 6 months after the first treatment. Women with precancerous changes caused by HPV infection may need further treatment. Young women and girls ages 9 - 26 shoul be vaccinated against HPV. Expectations (prognosis) Most sexually active young women become infected with HPV. In many cases, HPV goes away on its own. Most men who become infected with HPV never develop any symptoms or problems from the infection. However, they can pass it on to current and sometimes future sexual partners. Even after you have been treated for genital warts, you may still infect others. Certain types of genital warts increase a woman's risk for cancer of the cervix and vulva. Complications Some types of HPV have been found to cause cancer of the cervix and vulva. They are the main cause of cervical cancer. The types of HPV that can cause genital warts are not the same as the types that can cause penile or anal cancer. The warts may become numerous and quite large, requiring more extensive treatment and follow-up procedures. Prevention Total abstinence is the only foolproof way to avoid genital warts and other infections that are spread through sexual contact (STIs). You can also decrease your chance of getting an STI by having a sexual relationship with only one partner who you know is disease-free. Male and female condoms cannot fully protect you, because the virus or warts can be on the skin. Nonetheless, condoms reduce your risk and you should still use them at all times. HPV can be passed from person to person even when there are no visible warts or other symptoms. See: Safe sex Stop smoking. Two vaccines are available that protect against four of the HPV types that cause most cervical cancer in women. The vaccine is given as a series of three shots. It is recommended for girls and women ages 9 to 26. Epidemiology Genital HPV infections have an estimated prevalence in the US of 10–20% and clinical manifestations in 1% of the sexually active adult population.[16] US incidence of HPV infection has increased between 1975 and 2006.[16] About 80% of those infected are between the ages of 17–33.[16] Although treatments can remove the warts, they do not remove the HPV, so warts can recur after treatment (about 50–73% of the time[18]), and also spontaneously regress.[16] Traditional theories postulated that the virus remained in the body for a lifetime. However, new studies using sensitive DNA techniques have shown that through immunological response the virus can either be cleared or suppressed to levels below what polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests can measure. One study testing genital skin for subclinical HPV using PCR found a prevalence of 10%.[16]  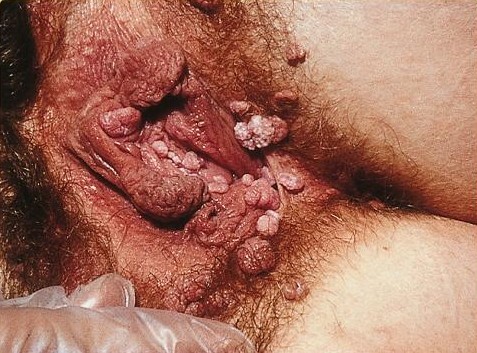
__________________
You are my forum, my only forum, you make me happy, when skies are grey... Sex health related questions click here. WOMEN'S CHARTER click here Sg law on sex related matters click here Last edited by Big Sexy; 04-05-2011 at 08:01 AM. |
|
#4
|
||||
|
||||
|
Re: All you need to know about STD ( with pictures)
Pubic Lice
What are pubic lice? Also called "crabs," pubic lice are parasitic insects found in the genital area of humans. Infection is common and found worldwide. How did I get pubic lice? Pubic lice are usually spread through sexual contact. Rarely, infestation can be spread through contact with an infested person's bed linens, towels, or clothes. A common misunderstanding is that infestation can be spread by sitting on a toilet seat. This isn't likely, since lice cannot live long away from a warm human body. Also, lice do not have feet designed to walk or hold onto smooth surfaces such as toilet seats. Infection in a young child or teenager may indicate sexual activity or sexual abuse.  Where are pubic lice found? Pubic lice are generally found in the genital area on pubic hair; but may occasionally be found on other coarse body hair, such as hair on the legs, armpits, mustache, beard, eyebrows, or eyelashes. Infestations of young children are usually on the eyebrows or eyelashes. Lice found on the head are not pubic lice; they are head lice. Animals do not get or spread pubic lice. What are the signs and symptoms of pubic lice? Signs and symptoms of pubic lice include Itching in the genital area Visible nits (lice eggs) or crawling lice What do pubic lice look like? There are three stages in the life of a pubic louse: the nit, the nymph, and the adult. Nit: Nits are pubic lice eggs. They are hard to see and are found firmly attached to the hair shaft. They are about the size of the mark at the end of this arrow . They are oval and usually yellow to white. Nits take about 1 week to hatch. Nymph: The nit hatches into a baby louse called a nymph. It looks like an adult pubic louse, but it is smaller. Nymphs mature into adults about 7 days after hatching. To live, the nymph must feed on blood. Adult: The adult pubic louse is about the size of this circle and resembles a miniature crab when viewed through a strong magnifying glass. Pubic lice have six legs, but their two front legs are very large and look like the pincher claws of a crab; this is how they got the nickname "crabs." Pubic lice are tan to grayish-white in color. Females lay nits and are usually larger than males. To live, adult lice must feed on blood. If the louse falls off a person, it dies within 1-2 days. How is a pubic lice infestation diagnosed? A lice infestation is diagnosed by looking closely through pubic hair for nits, nymphs, or adults. It may be difficult to find nymph or adult; here are usually few of them and they can move quickly away from light. If crawling lice are not seen, finding nits confirms that a person is infested and should be treated. If you are unsure about infestation or if treatment is not successful, see a health care provider for a diagnosis. How is a pubic lice infestation treated? A lice-killing shampoo (also called a pediculicide) made of 1% permethrin or pyrethrin is recommended to treat pubic lice. These products are available without a prescription at your local drug store. Medication is generally very effective; apply the medication exactly as directed on the bottle. A prescription medication, called Lindane (1%) is available through your health care provider. Lindane is not recommended for pregnant or nursing women, or for children less than 2 years old. Malathion* lotion 0.5% (Ovide*) is another prescription medication that is effective against pubic lice. How to treat pubic lice infestations: (Note: see section below for treatment of eyelashes or eyebrows. The lice medications described in this section should not be used near the eyes.) Wash the infested area; towel dry. Thoroughly saturate hair with lice medication. If using permethrin or pyrethrins, leave medication on for 10 minutes; if using Lindane, only leave on for 4 minutes. Thoroughly rinse off medication with water. Dry off with a clean towel. Following treatment, most nits will still be attached to hair shafts. Nits may be removed with fingernails. Put on clean underwear and clothing after treatment. To kill any lice or nits (attached to hairs) that may be left on clothing or bedding, machine-wash those washable items that the infested person used during the 2-3 days before treatment. Use the hot water cycle (130°F). Use the hot dryer cycle for at least 20 minutes. Dry-clean clothing that is not washable. Inform any sexual partners that they are at risk for infestation. Do not have sex until treatment is complete. Do not have sex with infected partners until partners have been treated and infestation has been cured. Repeat treatment in 7-10 days if lice are still found. To treat nits and lice found on eyebrows or eyelashes: If only a few nits are found, it may be possible to remove live lice and nits with your fingernails or a nit comb. If additional treatment is needed for pubic lice nits found on the eyelashes, applying an ophthalmic-grade petrolatum ointment (only available by prescription) to the eyelids twice a day for 10 days is effective. Vaseline* is a kind of petrolatum, but is likely to irritate the eyes if applied.
__________________
You are my forum, my only forum, you make me happy, when skies are grey... Sex health related questions click here. WOMEN'S CHARTER click here Sg law on sex related matters click here Last edited by Big Sexy; 03-05-2011 at 05:27 PM. |
|
#5
|
||||
|
||||
|
Re: All you need to know about STD ( with pictures)
Pubic Lice
source : http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001844/ Crab Louse, Female This is a photomicrograph of a female pubic louse. The condition known as "crabs" is so named because of the resemblance of a pubic louse to a crab. The bodies of pubic lice are shorter and rounder than those of head lice. (Courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control.)  Pubic louse-male This is a photomicrograph of a male pubic louse. The condition known as "crabs" is so named because of the resemblance of a pubic louse to a crab. The bodies of pubic lice are shorter and rounder than those of head lice.  This photograph shows pubic lice clinging to individual hairs (the small, whitish specks). The reddish, crusted areas with scabs (excoriated areas) are caused by scratching. (Courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control.)  this picture compares the relative size and shape of the head louse and the pubic louse. 
__________________
You are my forum, my only forum, you make me happy, when skies are grey... Sex health related questions click here. WOMEN'S CHARTER click here Sg law on sex related matters click here Last edited by Big Sexy; 03-05-2011 at 05:26 PM. |
|
#6
|
||||
|
||||
|
Re: All you need to know about STD ( with pictures)
Chancroid
source: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001659/ source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chancroid Chancroid (also known as Soft chancre[1]:274 and "Ulcus molle"[2]) is a sexually transmitted infection characterized by painful sores on the genitalia. Chancroid is known to be spread from one to another individual through sexual contact. Causes, incidence, and risk factors Chancroid is caused by a type of bacteria called Haemophilus ducreyi. The disease is found mainly in developing and third world countries. Only a small number of cases are diagnosed in the United States each year. Most people in the U.S. diagnosed with chancroid have traveled outside the country to areas where the disease is known to occur frequently. Uncircumcised men are at much higher risk than circumcised men for getting chancroid from an infected partner. Chancroid is a risk factor for the HIV virus. Symptoms Within 1 day - 2 weeks after getting chancroid, a person will get a small bump in the genitals. The bump becomes an ulcer within a day of its appearance. The ulcer: Ranges in size from 1/8 inch to 2 inches across Is painful Is soft Has sharply defined borders Has irregular or ragged borders Has a base that is covered with a grey or yellowish-grey material Has a base that bleeds easily if banged or scraped About half of infected men have only a single ulcer. Women often have 4 or more ulcers. The ulcers appear in specific locations. Common locations in men are: Foreskin (prepuce) Groove behind the head of the penis (coronal sulcus) Shaft of the penis Head of the penis (glans) Opening of the penis (urethral meatus) Scrotum In women the most common location for ulcers is the outer lips of the vagina (labia majora). "Kissing ulcers" may develop. These are ulcers that occur on opposite surfaces of the labia. Other areas such as the inner vagina lips (labia minora), the area between the genitals and the anus (perineal area), and inner thighs may also be involved. The most common symptoms in women are pain with urination and intercourse. The ulcer may look like a chancre, the typical sore of primary syphilis. Approximately half of the people infected with a chancroid will develop enlarged inguinal lymph nodes, the nodes located in the fold between the leg and the lower abdomen. Half of those who have swelling of the inguinal lymph nodes will progress to a point where the nodes break through the skin, producing draining abscesses. The swollen lymph nodes and abscesses are often referred to as buboes. Signs and tests Chancroid is diagnosed by looking at the ulcer(s) and checking for swollen lymph nodes. There are no blood tests for chancroid. Treatment The infection is treated with antibiotics, including azithromycin, ceftriaxone, ciprofloxacin, and erythromycin. Large lymph node swellings need to be drained, either with a needle or local surgery. Expectations (prognosis) Chancroid can get better on its own. However, some people may have months of painful ulcers and draining. Antibiotic treatment usually clears up the lesions quickly with very little scarring. Complications Complications include urethral fistulas and scars on the foreskin of the penis in uncircumcised males. Patients with chancroid should also be checked for syphilis, HIV, and genital herpes. Chancroids in persons with HIV may take much longer to heal. Prevention Chancroid is a bacterial infection that is spread by sexual contact with an infected person. Avoiding all forms of sexual activity is the only absolute way to prevent a sexually transmitted disease. However, safe sex behaviors may reduce your risk. The proper use of condoms, either the male or female type, greatly decreases the risk of catching a sexually transmitted disease. You need to wear the condom from the beginning to the end of each sexual activity.  
__________________
You are my forum, my only forum, you make me happy, when skies are grey... Sex health related questions click here. WOMEN'S CHARTER click here Sg law on sex related matters click here Last edited by Big Sexy; 04-05-2011 at 08:21 AM. |
|
#7
|
||||
|
||||
|
Re: All you need to know about STD ( with pictures)
CHLAMYDIA
Source: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0002321/ Chlamydia is a disease caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis. It is most commonly sexually transmitted. Causes, incidence, and risk factors Chlamydia infection is the most common sexually transmitted disease in the United States. Sexually active individuals and individuals with multiple partners are at highest risk. Symptoms As many as 1 in 4 men with chlamydia have no symptoms. In men, chlamydia may produce symptoms similar to gonorrhea. Symptoms may include: Burning sensation during urination Discharge from the penis or rectum Testicular tenderness or pain Rectal discharge or pain Only about 30% of women with chlamydia have symptoms. Symptoms that may occur in women include: Burning sensation during urination Painful sexual intercourse Rectal pain or discharge Symptoms of PID, salpingitis, liver inflammation similar to hepatitis Vaginal discharge See also: Chlamydia in women Signs and tests The diagnosis of chlamydia infection involves sampling of the urethral discharge in males or cervical secretions in females. If an individual engages in anal sexual contact, samples from the rectum may also be needed. The sample is sent for a fluorescent or monoclonal antibody test, DNA probe test, or cell culture. Some of these tests may also be performed on urine samples. Treatment The usual treatment for chlamydia is antibiotics, including tetracyclines, azithromycin, or erythromycin. You can get chlamydia with gonorrhea or syphilis, so if you have one sexually transmitted disease you must be screened for other sexually transmitted diseases as well. All sexual contacts should be screened for chlamydia. Sexual partners must be treated to prevent passing the infection back and forth. There is no significant immunity following the infection and a person may become repeatedly infected. A follow-up evaluation may be done in 4 weeks to determine if the infection has been cured. Expectations (prognosis) Early antibiotic treatment is extremely successful and may prevent the development of long-term complications. Untreated infection, however, may lead to complications. Complications Chlamydia infections in women may lead to inflammation of the cervix. In men, chlamydia infection can lead to inflammation of the urethra called urethritis. An untreated chlamydia infection may spread to the uterus or the fallopian tubes, causing salpingitis or pelvic inflammatory disease. These conditions can lead to infertility and increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy. If a women is infected with chlamydia while pregnant, the infection may cause infection in the uterus after delivery (late postpartum endometritis). In addition, the infant may develop chlamydia-related conjunctivitis (eye infection) and pneumonia. See: chlamydial pneumonia Because many people with chlamydia may not have symptoms, sexually active adults should be screened periodically for the infection. Prevention All sexually active women up through age 25 should be screened yearly for chlamydia. All women with new sexual partners or multiple partners should also be screened. A mutually monogamous sexual relationship with an uninfected partner is one way to avoid this infection. The proper use of condoms during intercourse usually prevents infection. 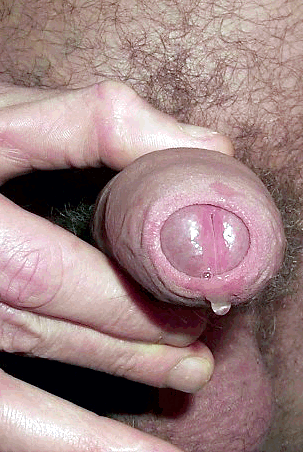 
__________________
You are my forum, my only forum, you make me happy, when skies are grey... Sex health related questions click here. WOMEN'S CHARTER click here Sg law on sex related matters click here Last edited by Big Sexy; 04-05-2011 at 08:38 AM. |
|
#8
|
||||
|
||||
|
Re: All you need to know about STD ( with pictures)
Chlamydia infections in women
Source:http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001681/ Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted disease. This article discusses chlamydia infections in women. See also: Chlamydia Chlamydial urethritis Causes, incidence, and risk factors Chlamydia is caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis. Different strains of chlamydia cause genital, eye, lymph node, and respiratory infections. A baby born to a woman with a chlamydia infection of the cervix may develop eye or lung infections. Chlamydia is transmitted through sexual activity. Sexually active individuals and individuals with multiple partners are at highest risk for chlamydia infections. Symptoms Abdominal pain Burning on urination Painful intercourse Vaginal discharge or bleeding after intercourse Note: Some women with chlamydia have no symptoms at all. Only some women will have symptoms. Therefore, screening sexually active women for chlamydia is necessary to diagnose and treat the condition in women who do not have symptoms. Signs and tests Diagnosing a chlamydia infection in a woman involves taking a sample of cervical secretions and sending it to a lab for an endocervical culture or a similar test called PCR. Chlamydia infection can be diagnosed with a urine test. Endocervical culture for gonorrhea may also be done. Treatment Chlamydia can be treated with a variety of antibiotics, including azithromycin, tetracyclines, quinolones, and erythromycin. Erythromycin and azithromycin are safe in pregnant women. Both sexual partners must be treated to prevent passing the infection back and forth between them, even though both may not have symptoms. Since gonorrhea often occurs along with chlamydia, treatment for gonorrhea is often given at the same time. Expectations (prognosis) Antibiotic treatment is usually successful. Reinfection may occur if you do not take your medicine as directed, or if your sexual partner is not treated. Complications Chlamydia infections in women may lead to inflammation of the cervix. An untreated chlamydia infection may spread to the uterus or the fallopian tubes, causing salpingitis or pelvic inflammatory disease. These conditions can lead to infertility and increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy. If a women has chlamydia while pregnant, it can lead to an infection in the uterus after delivery (late postpartum endometritis). In addition, the infant may develop chlamydia-related conjunctivitis (eye infection) and pneumonia. Calling your health care provider Call for an appointment with your health care provider if symptoms of chlamydia occur. Prevention All sexually active women up to age 25 should be screened yearly for chlamydia. All women with new sexual partners or multiple partners should also be screened. A mutually monogamous sexual relationship with an uninfected partner is one way to avoid this infection. The proper use of condoms during intercourse usually prevents infection.  
__________________
You are my forum, my only forum, you make me happy, when skies are grey... Sex health related questions click here. WOMEN'S CHARTER click here Sg law on sex related matters click here Last edited by Big Sexy; 04-05-2011 at 08:38 AM. |
|
#9
|
||||
|
||||
|
Re: All you need to know about STD ( with pictures)
Hepatitis C
Source: http://www.singhealth.com.sg/Patient...epatitisC.aspx What is hepatitis C? Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is an important cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. In some areas the prevalence of hepatitis C is extremely high, as in Egypt, Saudi Arabia, the Phillipines and Papua New Guinea. The prevalence of hepatitis C antibody in volunteer blood donors is generally estimated at between 0.4% and 1%. HCV has been described as the "shadow epidemic" because of the insidious nature of the infection which is generally asymptomatic and persists for life in 85% of patients infected with the virus. HCV has tremendous genetic diversity and this enables it to escape the surveillance of the immune system of infected individual thus leading to chronic infection. In the same light, there are difficulties in vaccine development. How is HCV transmitted? HCV is largely transmitted parenterally ie by blood and blood products. Therefore, HCV infections may be acquired via the following means: * Intravenous drug abuse * Tattooing * Body-piercing * Accidental needlestick injury * Hemodialysis in patients with kidney failure * Organ and semen donation from a HCV carrier * HCV can also be transmitted by snorting drugs like cocaine ( blood from damaged nasal mucosa and transmitted by sharing straws). * Vertical transmission ( mother to infant ) during childbirth is possible if the mother has a high HCV viral load, co-infection with HIV (AIDS) and has acute hepatitis C during pregnancy. There is a 6% transmission rate by this method. * Sexual transmission is possible if one engages in promiscuous sexual activity. * Rarely, household ( non sexual ) transmission is possible through the sharing of razors and toothbrushes. What is the clinical course after a HCV infection? The onset of infection is often unrecognised and the early course is generally indolent. The natural history of HCV infection is dependant upon on geography, alcohol use, viral characteristics ( different genetic types, viral load ), co-infection with other viruses and some as yet unidentified factors. After exposure to the virus, detectable viral genetic material called HCV RNA is seen in the blood in 1 - 3 weeks. Nearly all patients show evidence of liver injury because blood tests for liver enzymes become elevated. However, only 25% patients manifest symptoms like lassitude, anorexia and some became jaundiced (yellowing of eyes and skin). Rapid progression to liver failure due to fulminant hepatitis is a rare occurrence. The majority of patients (85%) fail to clear the virus within 6 months and develop chronic hepatitis C. These patients are relatively well in the first 2 decades after acquiring the infection. However in 20% of these carriers, there may be intermittent symptoms of fatigue and malaise. Symptoms Generally, symptoms only appear once advanced liver damage has occurred. These signs and symptoms are features of liver cirrhosis ("hardening of the liver tissue") which results from persistence of the hepatitis C virus. These include ascites (swelling of the abdomen with fluid), jaundice, deterioration of mental state (hepatic encephalopathy), vomiting blood or passing out altered blood in the stools. Of course, there is the dreaded complication of liver cancer. Generally, cirrhosis appears in at least 20% of patients within 20 years of infection. Cirrhosis can be accelerated by concomitant alcohol use. Liver cancer develops after 30 years and occurs only in a background of liver cirrhosis. It is interesting to note that hepatitis C has clinical manifestions beyond the liver. These are as a result of it's effect on the immune system, and are called extrahepatic manifestions. The extrahepatic manifestions include : * Joint swelling and pain ( arthritis ) * Eye inflammation ( keratoconjuretivitis sicca ) * Skin and oral manifestions ( lichen planus which appears as a characteristic rash and oral inflammation ). * Inflammation of kidneys ( glomerulonephritis ) * Essential mixed cryoglobulinemia - this last rare manifestion is in itself a rare disease which affects the blood and various other body systems. Major symptoms may include unusual response to cold, skin abnormalities, weakness and blood problems. There may be joint pain, inflammed blood vessels and kidney problems. Diagnosis Of interest is the fact that the origins of this virus is obscure, and had eluded identification for many years. A blood test for HCV identification was developed in 1990 and refined in 1992. The various blood tests available for HCV diagnosis are based on detection of antibody against HCV (EIA or enzymeimmunoassay and Recombinant immunoblot assays ( RIBAs ). Positive results means previous exposure to the hepatitis C virus. There are tests which detect the genetic material of the virus directly (polymerase chain reaction or PCR method) and this is a much more accurate blood test than antibody based test. EIA is inexpensive, reproducible and has been automated. It is a useful screening test. It's main failing is that is may not always be specific enough and false positive results can occur. This means positive results even the individuals do not have the infection. In a low risk population like in Singapore, a negative EIA test is sufficient to rule out infection. However if EIA is positive, RIBA is used to confirm the diagnosis of HCV infection. Another test done routinely is liver function tests. If these liver enzymes (ALT, AST) are elevated, it would indicate that there is liver inflammation. If this process is allowed to go unchecked, it will result in cirrhosis and liver cancer in the long run. Active liver disease caused by HCV requires further treatment to reduce the viral load. It is necessary to extract a small sample of the liver by a process known as a liver biopsy, for further examination in the laboratory. By studying the liver tissue one is able to assess the degree of inflammation and damage to liver. Liver biopsy is the gold standard for assessment of the activity of chronic hepatitis C. When combined with liver function tests, one can assess the severity or activity of the disease and institute treatment if necessary. Who should be tested for HCV infection? Individuals who : * Have had blood or blood product transfusion . * Are on hemodialysis * Have had multiple sexual partners * Are spouses or close household contacts of hepatitis C patients * Are organ transplant receipients * Share instruments for cocaine usage (eg. straws for snorting cocaine) Treatment Similar to hepatitis B, hepatitis C can lead to chronic hepatitis (liver inflammation), cirrhosis ( "liver hardening "), liver failure and liver cancer. Treatment is aimed at eradicating the virus and to prevent / delay it's complication. Alpha-Interferon: The current recommended regime for treatment is alpha-interferon 3 million units 3 times per week for 12 months. Interferon is administered subcutaneously. It is believed to act by obstructing viral replication and also boosting the immune system to destroy the virus. Flu like symptoms (fever, chills, malaise, headache, bone and muscle pain, rapid heart beat rate) are common in the initial part of treatment with interferon. Later side effects are fatigue, hair loss, suppression of white and red cell production, and psychiatric complications. Occasionally these patients may become irritable and depressed to the point of suicide. Severe side-effects occur in less than 2% of patients treated with interferon. These include thyroid problems, fits, heart and kidney failure, eye and lung problems, hearing impairment and infection. Rare deaths from liver failure or infection have occurred in some, especially those with cirrhosis. The milder side-effects of interferon may sometimes be ameliorated by administering interferon at night or taking paracetamol (Panadol). Occasionally a dose reduction or even discontinuation of treatment may be required in those with more severe side-effects. Following the initiation of interferon alfa therapy, the patient is monitored clinically and by blood tests. Visits to the liver specialist should be weekly initially (first month), followed by 2 to 4 weekly. If patients do not respond after 3months of therapy with interferon alone, they should be considered for combination therapy of interferon and ribavarin. Ribavarin is an oral anti-viral agent which is believed to act through inhibition of some effector of tissue damage. The main side-effect of this drug is the breakdown of red blood cells ( hemolysis ) resulting in anaemia ( low red blood cell count ). The response to interferon alfa therapy is between 20 & 30 percent. The goal of therapy is reduction of liver inflammation and the eradication of hepatitis C virus. What kind of surveilance will my doctor do to detect liver cancer? Although there is a lack of data supporting cost effectiveness, unlike in hepatitis B patients, patients with HCV cirrhosis should have a liver ultrasonography and serum alfa-fetoprotein level every 6 months for screening of liver cancer. Non-cirrhotic HCV carriers generally require 6 monthly alfa-fetoprotein levels and yearly ultrasonography of the liver.
__________________
You are my forum, my only forum, you make me happy, when skies are grey... Sex health related questions click here. WOMEN'S CHARTER click here Sg law on sex related matters click here Last edited by Big Sexy; 06-05-2011 at 09:19 AM. |
|
#10
|
||||
|
||||
|
Re: All you need to know about STD ( with pictures)
Hepatitis C
Source : http://www.singhealth.com.sg/Patient...epatitisC.aspx Who should receive treatment for HCV infection?] Patients with raised liver enzymes and liver biopsy indicating active inflammation. The role for intervention is strengthened if the patient's blood shows the presence of viral RNA ( HCV RNA ). * Patients with acute hepatitis C * Patients with HCV infection complicated by essential mixed cryoglobulinemia. * Patients with concurrent stable HIV infection, as these patients may have an accelerated course. Who should not be treated with interferon? * Patient with normal liver function tests * Patient with only mild symptoms like fatigue and no other clinical or laboratory abnormalities. * Patients who are drug abusers or active alcoholics. These patients are generally not compliant and should therefore receive treatment for substance abuse before commencing HCV therapy. * Patients with major psychiatric illness. * Patients with hyperthyroidism. * Patients with blood disorders * Patients with abnormalities of the immune system eg. systemic lupus erythematosis * Patients who have had a renal transplant and is currently receiving immunosuppressive treatment to prevent graft rejection. Prevention * HCV positive carriers should avoid donating blood, tissue, organs or semen. * Safer sexual practices should be strongly encouraged in persons with multiple sexual partners eg. by using latex condoms. * Avoid sharing razors and toothbrushes with members of the household who are HCV carriers. * Intravenous drug users should not share needles/syringes. * Pregnancy is not contraindicated in HCV carriers. However the child should be tested for antibodies against HCV at one year of age.
__________________
You are my forum, my only forum, you make me happy, when skies are grey... Sex health related questions click here. WOMEN'S CHARTER click here Sg law on sex related matters click here Last edited by Big Sexy; 06-05-2011 at 09:19 AM. |
|
#11
|
||||
|
||||
|
Re: All you need to know about STD ( with pictures)
Gonorrhea (clap, drip)
Source :http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0004526/ Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gonorrhea Causes, incidence, and risk factors Gonorrhea is caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Anyone who has any type of sex can catch gonorrhea. The infection can be spread by contact with the mouth, vagina, penis, or anus. The bacteria grow in warm, moist areas of the body, including the tube that carries urine out of the body (urethra). In women, the bacteria may be found in the reproductive tract (which includes the fallopian tubes, uterus, and cervix). The bacteria can even grow in the eyes. Health care providers in every state in the U.S. are required by law to tell their State Board of Health about anyone diagnosed with gonorrhea. The goal of this law is make sure the patient gets proper follow-up care and that their sexual partners are found and tested. More than 700,000 persons in the United States get gonorrhea every year, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Gonorrhea is more common in large cities, inner-city areas, populations with lower overall levels of education and people with lower socioeconomic status. You are more likely to develop this infection if you: Have multiple sexual partners Have a partner with a past history of any sexually transmitted disease Do not use a condom during sex Have a drug addiction Symptoms Symptoms of gonorrhea usually appear 2 - 5 days after infection, however, in men, symptoms may take up to a month to appear. Some people do not have symptoms. They may be completely unaware that they have caught the disease, and therefore do not seek treatment. This increases the risk of complications and the chances of passing the infection on to another person. Symptoms in men include: Burning and pain while urinating Increased urinary frequency or urgency Discharge from the penis (white, yellow, or green in color) Red or swollen opening of penis (urethra) Tender or swollen testicles Sore throat (gonococcal pharyngitis) Symptoms in women can be very mild or nonspecific, and may be mistaken for another type of infection. They include: Vaginal discharge Burning and pain while urinating Increased urination Sore throat Painful sexual intercourse Severe pain in lower abdomen (if the infection spreads to the fallopian tubes and stomach area) Fever (if the infection spreads to the fallopian tubes and stomach area) If the infection spreads to the bloodstream, fever, rash, and arthritis-like symptoms may occur. See: Disseminated gonococcemia Signs and tests Gonorrhea can be quickly identified by staining a sample of tissue or discharge and then looking at it under a microscope. This is called a gram stain. Although this method is fast, it is not the most certain. Gram stain tests used to diagnose gonorrhea include: Cervical gram stain in women Gram stain of urethral discharge in men Joint fluid gram stain Cultures (cells that grow in a lab dish) provide absolute proof of infection. Generally, samples for a culture are taken from the cervix, vagina, urethra, anus, or throat. Cultures can provide a preliminary diagnosis often within 24 hours and a confirmed diagnosis within 72 hours. Cultures used to diagnose gonorrhea include: Endocervical culture in women Urethral discharge culture in men Throat swab culture in both men and women Rectal culture in both men and women Culture of joint fluid Blood cultures DNA tests are especially useful as a screening test. They included the ligase chain reaction (LCR) test. DNA tests are quicker than cultures. Such tests can be performed on urine samples, which are a lot easier to collect than samples from the genital area. Treatment There are two goals in treating a sexually transmitted disease, especially one as easily spread as gonorrhea. The first is to cure the infection in the patient. The second is to locate and test all of the other people the person had sexual contact with and treat them to prevent further spread of the disease. Never treat yourself without being seen by your doctor first. Your health care provider will determine the best and most up-to-date treatment. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends the following treatments for uncomplicated gonorrhea. A single shot of ceftriaxone (Rocephin) 125 mg or a single dose of cefixime 400 mg taken by mouth are currently the recommended antibiotic treatment Azithromycin (Zithromax) 2g in a single dose may be used for people who have severe allergic reactions to ceftriaxone, cefixime, or penicillin. Penicillin used to be the standard treatment, but it is not used any longer because it does not cure gonorrhea all the time. The CDC also recommendeds against using a class of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, or levofloxacin). Persons with gonorrhea often also have a chlamydia infection. If a chlamydia culture was not done to rule out this infection, a single dose of azithromycin (1g by mouth) or doxycycline 100 mg twice a day, by mouth for 7 days should also be given. A follow-up visit 7 days after treatment is important if joint pain, skin rash, or more severe pelvic or belly pain is present. Tests will be done to make sure the infection is gone. All sexual contacts of the person with gonorrhea should be contacted and tested. This helps prevent further spread of the disease. In some places you may be able to take counseling information and medicines to your sexual partner yourself. In other places, the health department will contact your partner. Expectations (prognosis) Immediately treating a gonorrhea infection helps prevent permanent scarring and infertility. When treatment is delayed there is a greater chance of complications and sterility. About half of the women with gonorrhea are also infected with chlamydia, another very common sexually transmitted disease that can result in sterility. Chlamydia is treated at the same time as a gonorrhea infection. If you have gonorrhea, you should ask to be tested for other sexually transmitted diseases, including chlamydia, syphilis, and HIV. You should also receive the hepatitis B vaccine. Complications Complications in women may include: Salpingitis (scarring of the fallopian tubes), which can lead to problems getting pregnant or ectopic pregnancy Pelvic inflammatory disease Sterility (inability to become pregnant) Painful intercourse (dyspareunia) Pregnant women with severe gonorrhea may pass the disease to their baby while in the womb or during delivery Complications in men may include: Scarring or narrowing of the urethra, the tube that carries urine out of the body (See: Urethral stricture) Abscess (collection of pus around the urethra) Urination problems Urinary tract infection Kidney failure Complications in both men and women may include: Disseminated infection, which can be very serious Long-term joint pain, if the infection is left untreated Heart valve infection Meningitis Prevention Not having sexual intercourse (abstinence) is the only absolute method of preventing gonorrhea. A monogamous sexual relationship with an individual known to be free of any STD can reduce risk. Monogamous means you and your partner do not have sex with any other persons. You can greatly lower your risk of catching an STD by using a condom every time you have sex. Condoms are available for both men and women, but are most commonly worn by the man. A condom must be used properly every time. (For instructions on how to use a condom, see safe sex.) Epidemiology Gonorrhea is a common infectious disease. In the United Kingdom 196 per 100,000 males 20-24 year old, and 133 per 100,000 females 16-19 year were diagnosed in 2005.[2] The CDC estimates that more than 700,000 people in the United States get new gonorrheal infections each year. Only about half of these infections are reported to CDC. In 2004, 330,132 cases of gonorrhea were reported to the CDC. After the implementation of a national gonorrhea control program in the mid-1970s, the national gonorrhea rate declined from 1975 to 1997. After a small increase in 1998, the gonorrhea rate has decreased slightly since 1999. In 2004, the rate of reported gonorrheal infections was 113.5 per 100,000 persons.[15] In the US, it is the second most common bacterial sexually transmitted infections after chlamydia[16][17]   
__________________
You are my forum, my only forum, you make me happy, when skies are grey... Sex health related questions click here. WOMEN'S CHARTER click here Sg law on sex related matters click here Last edited by Big Sexy; 04-05-2011 at 09:30 AM. |
|
#12
|
||||
|
||||
|
Re: All you need to know about STD ( with pictures)
Hepatitis B
Source: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001324/ Source: http://www.hepb.org/hepb/statistics.htm Source: http://gsk.com.my/pharma-antivirals-hepatitis.html Hepatitis B is irritation and swelling (inflammation) of the liver due to infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Causes, incidence, and risk factors Hepatitis B infection can be spread through having contact with the blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and other body fluids of someone who already has a hepatitis B infection. Infection can be spread through: * Blood transfusions (not common in the United States) * Direct contact with blood in health care settings * Sexual contact with an infected person * Tattoo or acupuncture with unclean needles or instruments * Shared needles during drug use * Shared personal items (such as toothbrushes, razors, and nail clippers) with an infected person The hepatitis B virus can be passed to an infant during childbirth if the mother is infected. Most of the damage from the hepatitis B virus occurs because of the way the body responds to the infection. When the body's immune system detects the infection, it sends out special cells to fight it off. However, these disease-fighting cells can lead to liver inflammation. Symptoms After you first become infected with the hepatitis B virus: * You may have no symptoms * You may feel sick for a period of days or weeks * You may become very ill (called fulminant hepatitis) If your body is able to fight off the hepatitis B infection, any symptoms that you had should go away over a period of weeks to months. Some people's bodies are not able to completely get rid of the hepatitis B infection. This is called chronic hepatitis B. Many people who have chronic hepatitis B have few or no symptoms. They may not even look sick. As a result, they may not know they are infected. However, they can still spread the virus to other people. Symptoms may not appear for up to 6 months after the time of infection. Early symptoms may include: * Appetite loss * Fatigue * Fever, low-grade * Muscle and joint aches * Nausea and vomiting * Yellow skin and dark urine due to jaundice People with chronic hepatitis may have no symptoms, even though gradual liver damage may be occurring. Over time, some people may develop symptoms of chronic liver damage and cirrhosis of the liver. Signs and tests The following tests are done to identify and monitor liver damage from hepatitis B: * Albumin level * Liver function tests * Prothrombin time The following tests are done to help diagnose and monitor people with hepatitis B: * Antibody to HBsAg (Anti-HBs) -- a positive result means you have either had hepatitis B in the past, or have received a hepatitis B vaccine * Antibody to hepatitis B core antigen (Anti-HBc) -- a positive result means you had a recent infection or an infection in the past * Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) -- a positive result means you have an active infection * Hepatitis E surface antigen (HBeAg) -- a positive result means you have a hepatitis B infection and are more likely to spread the infection to others through sexual contact or sharing needles Patients with chronic hepatitis will need ongoing blood tests to monitor their status. Treatment Acute hepatitis needs no treatment other than careful monitoring of liver and other body functions with blood tests. You should get plenty of bed rest, drink plenty of fluids, and eat healthy foods. In the rare case that you develop liver failure, you may need a liver transplant. A liver transplant is the only cure in some cases of liver failure. Some patients with chronic hepatitis may be treated with antiviral medications or a medication called peginterferon. These medications can decrease or remove hepatitis B from the blood and reduce the risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer. Liver transplantation is used to treat severe, chronic hepatitis B liver disease. Patients with chronic hepatitis should avoid alcohol and should always check with their doctor or nurse before taking any over-the-counter medications or herbal supplements. This even includes medications such as acetaminophen, aspirin, or ibuprofen. See: Cirrhosis for information about treating more severe liver damage caused by hepatitis B. Expectations (prognosis) The acute illness usually goes away after 2 - 3 weeks. The liver usually returns to normal within 4 - 6 months in almost all patients who are infected. Some people develop chronic hepatitis. * Almost all newborns and about 50% of children who become infected with hepatitis B develop chronic hepatitis. Less than 5% of adults who are infected with the hepatitis B virus develop the chronic condition. * Chronic hepatitis B infection increases the risk for liver damage, including cirrhosis and liver cancer. * People who have chronic hepatitis B can transmit the infection. They are considered carriers of the disease, even if they do not have any symptoms. Hepatitis B is fatal in about 1% of cases. Complications There is a much higher rate of hepatocellular carcinoma in people who have chronic hepatitis B than in the general population. Other complications may include: * Chronic persistent hepatitis * Cirrhosis * Fulminant hepatitis, which can lead to liver failure and possibly death Calling your health care provider Call your health care provider if: * You develop symptoms of hepatitis B * Hepatitis B symptoms do not go away in 2 or 3 weeks, or new symptoms develop * You belong to a high-risk group for hepatitis B and have not yet received the HBV vaccine. Prevention All children should receive their first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine at birth, and complete the series of three shots by age 6 months. Children younger than age 19 who have not been vaccinated should receive "catch-up" doses. People who are at high risk, including health care workers and those who live with someone who has hepatitis B should get the hepatitis B vaccine. Infants born to mothers who either currently have acute hepatitis B, or who have had the infection should receive a special vaccination that includes hepatitis B immune globulin and a hepatitis B immunization within 12 hours of birth. Screening of all donated blood has reduced the chance of getting hepatitis B from a blood transfusion. Mandatory reporting of the disease allows state health care workers to track people who have been exposed to the virus. The vaccine is given to those who have not yet developed the disease. The hepatitis B vaccine or a hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) shot may help prevent hepatitis B infection if it is given within 24 hours of exposure. Lifestyle measures for preventing transmission of hepatitis B: * Avoid sexual contact with a person who has acute or chronic hepatitis B. * Use a condom and practice safe sex. * Avoid sharing personal items, such as razors or toothbrushes. * Do not share drug needles or other drug equipment (such as straws for snorting drugs). * Clean blood spills with a solution containing 1 part household bleach to 10 parts water. Statistics Most healthy adults (90%) who are infected will recover and develop protective antibodies against future hepatitis B infections. A small number (5-10%) will be unable to get rid of the virus and will develop chronic infections. Unfortunately, this is not true for infants and young children – 90% of infants and up to 50% of young children infected with hepatitis B will develop chronic infections. Therefore, vaccination is essential to protect infants and children. Hepatitis B is 100 times more infectious than the AIDS virus, yet it can be prevented with a safe and effective vaccine. For the 400 million people worldwide who are already chronically infected with hepatitis B, the vaccine is of no use. The future, however, is much brighter with the current advances in drug development and treatment options. Hepatitis B In the World * 2 billion people have been infected (1 out of 3 people). * 400 million people are chronically infected. * 10-30 million will become infected each year. * An estimated 1 million people die each year from hepatitis B and its complications. * Approximately 2 people die each minute from hepatitis B.  A COMPARISON OF HIV AND HBV 
__________________
You are my forum, my only forum, you make me happy, when skies are grey... Sex health related questions click here. WOMEN'S CHARTER click here Sg law on sex related matters click here Last edited by Big Sexy; 06-05-2011 at 07:37 AM. |
|
#13
|
||||
|
||||
|
Re: All you need to know about STD ( with pictures)
What is TRICHOMONIASIS
Source:http://www.cdc.gov/std/trichomonas/s...homoniasis.htm Source:http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0002307/ Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. Trichomoniasis is a common sexually transmitted disease (STD) that affects both women and men, although symptoms are more common in women. Causes, incidence, and risk factors Trichomoniasis is found worldwide. In the United States, the highest number of cases are seen in women between age 16 and 35. Trichomonas vaginalis is spread through sexual contact with an infected partner. This include penis-to-vagina intercourse or vulva-to-vulva contact. The parasite cannot survive in the mouth or rectum. The disease can affect both men and women, but the symptoms differ between the two groups. The infection usually does not cause symptoms in men and goes away on its own in a few weeks. Symptoms Women: Discomfort with intercourse Itching of the inner thighs Vaginal discharge (thin, greenish-yellow, frothy or foamy) Vaginal itching Vulvar itching or swelling of the labia Vaginal odor (foul or strong smell) Men: Burning after urination or ejaculation Itching of urethra Slight discharge from urethra Occasionally, some men with trichomoniasis may develop prostatitis or epididymitis from the infection. Signs and tests In women: A pelvic examination shows red blotches on the vaginal wall or cervix. A wet prep (microscopic examination of discharge) shows the infection-causing organisms in vaginal fluids. A pap smear may also diagnose the condition. In men: The disease can be hard to diagnose in men. Men are treated if the infection is diagnosed in any of their sexual partners. Men may also be treated if they have ongoing symptoms of urethral burning or itching despite treatment for gonorrhea and chlamydia. Treatment The antibiotic metronidazole is commonly used to cure the infection. A newer drug, called Tinidazole may be used. You should not drink alcohol while taking the medicine and for 48 hours afterwards. Doing so can cause severe nausea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Avoid sexual intercourse until treatment has been completed. Sexual partners should be treated at the same time, even if they have no symptoms. Expectations (prognosis) With proper treatment, the outcome is likely to be excellent. Complications Long-term infection may cause changes in the tissue on the cervix. These changes may be seen on a routine Pap smear. In such cases, treatment should be started and the Pap smear repeated 3 to 6 months later. Treatment of trichomoniasis helps prevents the spread of the disease to sexual partners. Trichomoniasis is common among persons with HIV. Prevention A monogamous sexual relationship with a known healthy partner can help reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections, including trichomoniasis. Other than total abstinence, condoms remain the best and most reliable protection against sexually transmitted infections. Condoms must be used consistently and correctly to be effective. How does trichomoniasis affect a pregnant woman and her baby? Pregnant women with trichomoniasis may have babies who are born early or with low birth weight (low birth weight is less than 5.5 pounds).  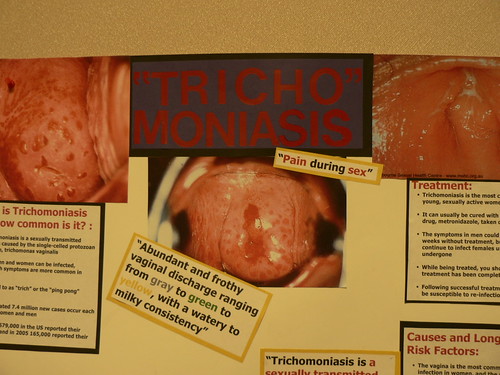
__________________
You are my forum, my only forum, you make me happy, when skies are grey... Sex health related questions click here. WOMEN'S CHARTER click here Sg law on sex related matters click here Last edited by Big Sexy; 04-05-2011 at 10:31 AM. |
|
#14
|
||||
|
||||
|
Re: All you need to know about STD ( with pictures)
Molluscum contagiosum
Source :http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001829/ Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Molluscum_contagiosum Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection that causes raised, pearl-like papules or nodules on the skin. Causes, incidence, and risk factors Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a virus that is a member of the poxvirus family. You can get the infection in a number of different ways. This is a common infection in children and occurs when a child comes into direct contact with a lesion. It is frequently seen on the face, neck, armpit, arms, and hands but may occur anywhere on the body except the palms and soles. The virus can spread through contact with contaminated objects, such as towels, clothing, or toys. The virus also spreads by sexual contact. Early lesions on the genitalia may be mistaken for herpes or warts but, unlike herpes, these lesions are painless. Persons with a weakened immune system (due to conditions such as AIDS) may have a rapidly worse case of molluscum contagiosum. Symptoms Typically, the lesion of molluscum begins as a small, painless papule that may become raised up to a pearly, flesh-colored nodule. The papule often has a dimple in the center. These papules may occur in lines, where the person has scratched. Scratching or other irritation causes the virus to spread in a line or in groups, called crops. The papules are about 2 - 5 millimeters wide. There is usually no inflammation and subsequently no redness unless you have been digging or scratching at the lesions. The skin lesion commonly has a central core or plug of white, cheesy or waxy material. In adults, the lesions are commonly seen on the genitals, abdomen, and inner thigh. Signs and tests Diagnosis is based on the appearance of the lesion and can be confirmed by a skin biopsy. The health care provider should examine the lesion to rule out other disorders and to determine other underlying disorders. Treatment Individual molluscum lesions may go away on their own and are reported as lasting generally from 6 to 8 weeks,[4] to 2 or 3 months.[5] However via autoinoculation, the disease may propagate and so an outbreak generally lasts longer with mean durations variously reported as 8 months,[4] to about 18 months,[6][7] and with a range of durations from 6 months to 5 years.[5][7] Treatment is often unnecessary[8] depending on the location and number of lesions, and no single approach has been convincingly shown to be effective. It should also be noted that treatments causing the skin on or near the lesions to rupture may spread the infection further, much the same as scratching does.[9] Nonetheless, treatment may be sought for the following reasons: Molluscum lesions on an arm. * Medical issues including: o Bleeding o Secondary infections o Itching and discomfort o Potential scarring o Chronic keratoconjunctivitis * Social reasons o Cosmetic o Embarrassment o Fear of transmission to others o Social exclusion Many health professionals recommend treating bumps located in the genital area to prevent them from spreading.[7] The virus lives only in the skin and once the growths are gone, the virus is gone and cannot be spread to others. When treatment has resulted in elimination of all bumps, the infection has been effectively cured and will not reappear unless the patient is reinfected.[10] In practice, it may not be easy to see all of the molluscum contagiosum bumps. Even though they appear to be gone, there may be some that were overlooked. If this is the case, one may develop new bumps by autoinoculation, despite their apparent absence. Expectations (prognosis) Molluscum contagiosum lesions may persist from a few months to a few years. These lesions ultimately disappear without scarring, unless there is excessive scratching, which may leave marks. Individual lesions usually disappear within about 2 - 3 months. Complete disappearance of all lesions generally occurs within about 6 - 18 months. The disorder may persist in immunosuppressed people. Complications Persistence, spread, or recurrence of lesions Secondary bacterial skin infections Calling your health care provider Call for an appointment with your health care provider if you have symptoms suggestive of molluscum contagiosum. Also call for an appointment with your health care provider if lesions persist or spread, or if new symptoms appear. Prevention Avoid direct contact with the skin lesions. Do not share towels with other people. Avoiding sex can also prevent molluscum virus and other STDs. You can also avoid STDs by having a monogamous sexual relationship with a partner known to be disease-free. Male and female condoms cannot fully protect you, as the virus can be on areas not covered by the condom. Nonetheless, condoms should still be used every time the disease status of a sexual partner is unknown. They reduce your chances of getting or spreading STDs. Use them with spermicide with nonoxynol 9.  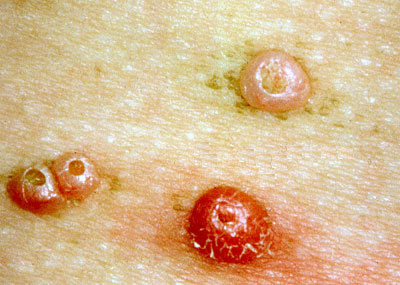
__________________
You are my forum, my only forum, you make me happy, when skies are grey... Sex health related questions click here. WOMEN'S CHARTER click here Sg law on sex related matters click here Last edited by Big Sexy; 04-05-2011 at 11:28 AM. |
|
#15
|
||||
|
||||
|
Re: All you need to know about STD ( with pictures)
Molluscum-Transmission
The virus is transmitted by: Direct skin-to-skin contact with infected skin Manual contact, such as sharing towels and sports/locker room equipment Nonsexual, intimate contact Scratching, picking or breaking the blisters and touching one another (especially in preschool and elementary school children) Vaginal, anal, and oral intercourse  Molluscum-Diagnosis Diagnosis is usually ascertained by: Observation of the classical skin lesion Tissue taken from the sore and examined under a microscope |
| Advert Space Available |
 |
| Bookmarks |
|
|